Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone playing a crucial role in glucose metabolism and insulin secretion. Recently, its benefits have extended beyond diabetes management, showing promise in cardiovascular disease prevention and hormonal balance. This article explores the multifaceted role of GLP-1 and its therapeutic potential.
GLP-1 in Cardiovascular Health
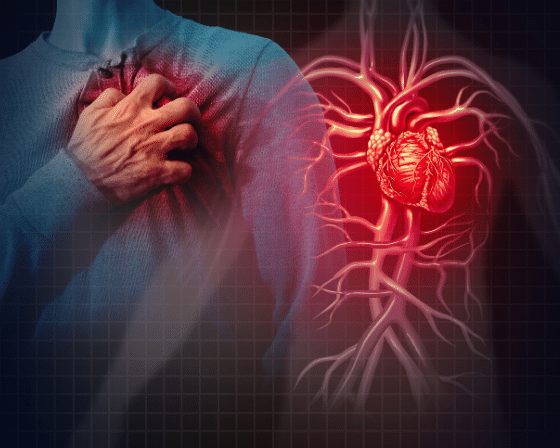
GLP-1 agonists, initially developed for type 2 diabetes, have shown remarkable benefits in cardiovascular health. These drugs not only help in glycemic control but also positively impact blood pressure, lipid metabolism, and weight management.
Clinical trials like the LEADER and SUSTAIN-6 have demonstrated that GLP-1 agonists can reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including heart attack and stroke, in individuals with type 2 diabetes. The mechanism behind this protective effect is multifaceted – ranging from improved endothelial function to reduced inflammation and atherosclerosis.
GLP-1 and Hormonal Imbalances
The role of GLP-1 extends to addressing hormonal imbalances related to metabolic syndrome, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. By enhancing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon release, GLP-1 helps in regulating blood glucose levels more effectively.
Moreover, GLP-1 impacts appetite and gastric emptying, contributing to weight loss – a significant factor in managing hormonal imbalances. This makes GLP-1 agonists a valuable tool not only for diabetes management but also for treating conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), where weight management plays a crucial role.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising benefits, GLP-1 based therapies come with challenges. Gastrointestinal side effects are common, and there is a need for long-term studies to understand the implications of prolonged GLP-1 receptor activation.
The future of GLP-1 therapy looks towards developing more effective and well-tolerated agonists and exploring their potential in non-diabetic populations for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Conclusion
GLP-1 has emerged as a cornerstone in the management of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Its role in hormonal balance further highlights its significance in metabolic health. As research continues to evolve, GLP-1 based therapies hold the potential to transform the landscape of treatment for metabolic and cardiovascular disorders, offering a more holistic approach to managing these interrelated conditions.